Seminars / Lectures
-
World Meteorological Day Special Lecture

Dr. K.J. Ramesh (Senior Advisor, RIMES, Asian Institute of Technology, Bangkok, Former Director General of Meteorology, IMD; Former Member (Technical) of CAQM NCR Delhi, Adjunct Professor, NIAS, Bengaluru) - Prof. R. Ananthakrishnan Seminar Series
- PhD Proposal/Synopsis seminars
-
Lecture Series on
Cloud and Precipitation Physics and Dynamics
New Report by IITM Scientists
General Document on Common Questions and Answers on Cloud Seeding
IITM Publication Highlights
Dengue dynamics, predictions, and future increase under changing monsoon climate in India
 The study investigates climate-dengue linkages and leverages AI/ML to develop an early warning
system and future dengue projections for Pune. This was a challenging effort, given the difficulty
in accessing health data and the transdisciplinary nature of the study. The findings indicate that
during the monsoon season (June–September), a combination of warm temperatures above
27°C, moderate and evenly distributed rainfall, and humidity levels between 60% and 78%
increases dengue incidence and mortality. Conversely, heavy rainfall exceeding 150 mm in a week
helps reduce dengue prevalence by flushing out mosquito eggs and larvae. Under low-to-high fossil
fuel emissions scenarios, dengue cases in Pune are projected to rise by 13% in the near term.
The study investigates climate-dengue linkages and leverages AI/ML to develop an early warning
system and future dengue projections for Pune. This was a challenging effort, given the difficulty
in accessing health data and the transdisciplinary nature of the study. The findings indicate that
during the monsoon season (June–September), a combination of warm temperatures above
27°C, moderate and evenly distributed rainfall, and humidity levels between 60% and 78%
increases dengue incidence and mortality. Conversely, heavy rainfall exceeding 150 mm in a week
helps reduce dengue prevalence by flushing out mosquito eggs and larvae. Under low-to-high fossil
fuel emissions scenarios, dengue cases in Pune are projected to rise by 13% in the near term.
The study has received significant coverage, and we are now seeing increased willingness from health departments to share data—an encouraging step toward better public health preparedness.
(Sophia Y., Roxy M.K., Murtugudde R., Karipot A., Sapkota A., Dasgupta P., …, Chattopadhyay R., … et al., Scientific Reports, 15: 1637, January 2025, DOI:10.1038/s41598-025-85437-w, 1-16 )
Read MoreIndian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) High-Resolution Global Forecast Model version 1: an attempt to resolve monsoon prediction deadlock
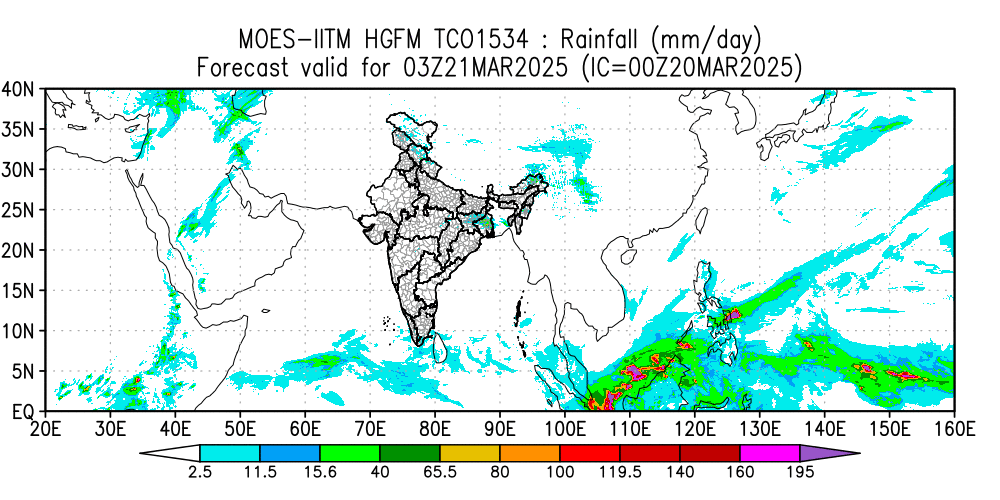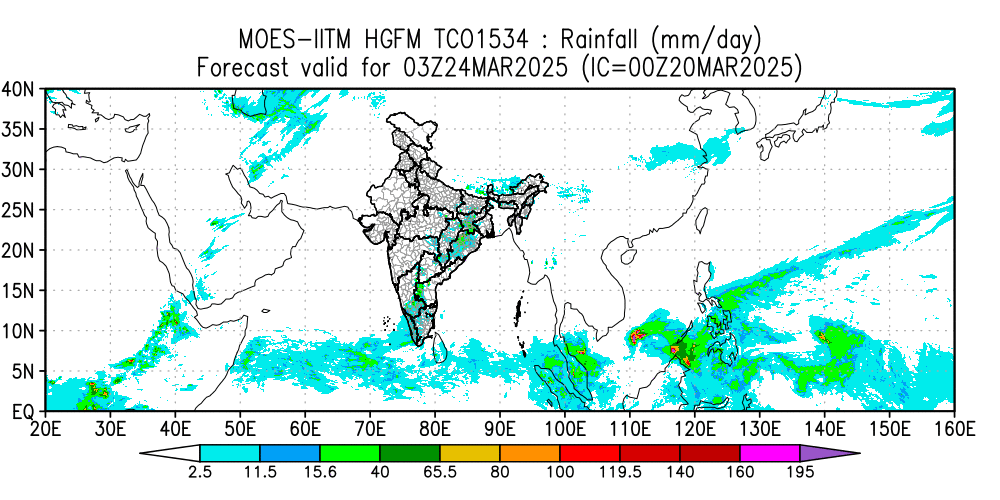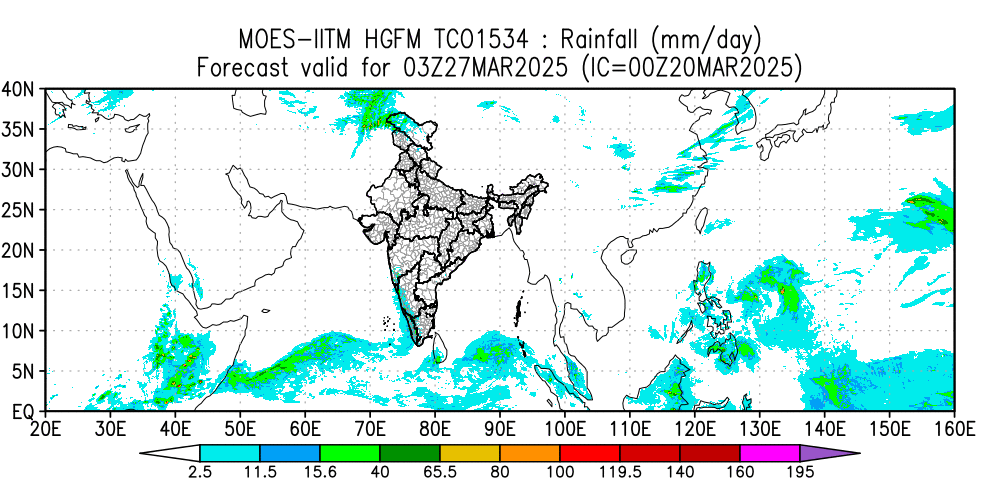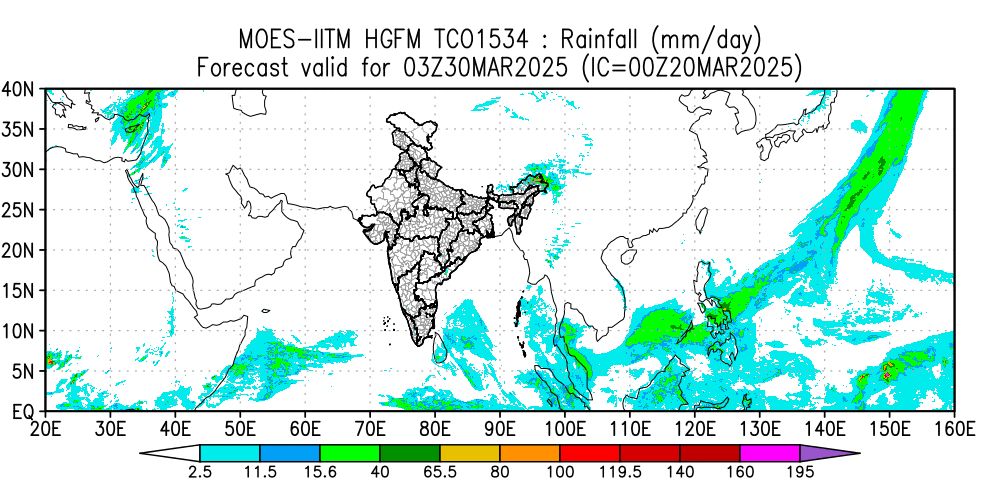
 This paper highlights the initial results of the newly developed HGFM and its skill compared to the operational GFS T1534 model. An attempt is made to develop a global model using a dynamic core of a cubic octahedral grid that provides a higher resolution of 6.5 km over the global tropics. This high-resolution model has been developed to resolve the monsoon convection. Reforecasts with the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) High-Resolution Global Forecast Model (HGFM) have been run daily from June through September 2022. HGFM has a wavenumber truncation of 1534 in the cubic octahedral grid. The monsoon events have been predicted with a 10 d lead time. HGFM is compared to the operational Global Forecast System (GFS) T1534. While HGFM provides skills comparable to GFS, it shows better skills for higher precipitation thresholds. This model is currently being run in experimental mode and will be made operational.
This paper highlights the initial results of the newly developed HGFM and its skill compared to the operational GFS T1534 model. An attempt is made to develop a global model using a dynamic core of a cubic octahedral grid that provides a higher resolution of 6.5 km over the global tropics. This high-resolution model has been developed to resolve the monsoon convection. Reforecasts with the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) High-Resolution Global Forecast Model (HGFM) have been run daily from June through September 2022. HGFM has a wavenumber truncation of 1534 in the cubic octahedral grid. The monsoon events have been predicted with a 10 d lead time. HGFM is compared to the operational Global Forecast System (GFS) T1534. While HGFM provides skills comparable to GFS, it shows better skills for higher precipitation thresholds. This model is currently being run in experimental mode and will be made operational.
(Phani M.K.R., Kumar Siddharth, Prajeesh A.G., Bechtold P., Wedi N., Roy K., Ganai M., Reddy B.R., Tirkey S., Goswami T., Kanase R., Sarkar S., Deshpande M., Mukhopadhyay P., Geoscientific Model Development, 18, March 2025, DOI:10.5194/gmd-18-1879-2025, 1879-1894)
Read MoreSpatiotemporal variations in the characteristics of mesoscale convective systems over Indian monsoon zone
 In this work, various crucial attributes of mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), including spatial coverage, diurnal progression, rainfall volume, and land-ocean difference, are examined by tracking MCSs using high-resolution satellite data of cloud and precipitation. Most MCSs are in the southeast-northwest strip of monsoon trough and account for over 60% of total precipitation. There was an apparent land-ocean dichotomy and different lifecycle progression for MCSs with short and long lifespans. Oceanic MCSs endure longer, grow larger, and deliver more rainfall over a greater region than those over land. The sensitivity of MCS precipitation to environmental moisture and wind shear is substantially higher over BoB than those over land. The structural and evolution-based diagnosis of monsoonal MCSs reported in this work could help evaluate model simulations.
In this work, various crucial attributes of mesoscale convective systems (MCSs), including spatial coverage, diurnal progression, rainfall volume, and land-ocean difference, are examined by tracking MCSs using high-resolution satellite data of cloud and precipitation. Most MCSs are in the southeast-northwest strip of monsoon trough and account for over 60% of total precipitation. There was an apparent land-ocean dichotomy and different lifecycle progression for MCSs with short and long lifespans. Oceanic MCSs endure longer, grow larger, and deliver more rainfall over a greater region than those over land. The sensitivity of MCS precipitation to environmental moisture and wind shear is substantially higher over BoB than those over land. The structural and evolution-based diagnosis of monsoonal MCSs reported in this work could help evaluate model simulations.
(Tupsoundare M., Deshpande S.M., Feng Z., Das S.K., Deshpande M., Hanmante H., Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 130: e2024JD042344, February 2025, DOI:10.1029/2024JD042344, 1-27)
Read MoreSimulating rainfall during thunderstorm events: Insights into cloud-to-rain microphysical processes over the Indian subcontinent
 The study investigates the performance of autoconversion in cloud microphysical schemes within high-resolution numerical models. The liquid water content and cloud properties, varying from shallow to convective clouds, are highly sensitive to autoconversion rates, and their sensitivity is closely linked with model biases. Four different (Kessler, KES; Liu-Daum, LD; Khairoutdinov-Kogan, KK; Lee-Baik, LB) autoconversion parameterization schemes have been utilized in the WRF model for simulating two thunderstorm events over India. The LD, LB and KK autoconversion rates exhibited closer performance and demonstrated a better probability distribution of raindrop size and precipitation compared to KES. The study highlights the importance of proper choice of autoconversion rates in numerical weather prediction models.
The study investigates the performance of autoconversion in cloud microphysical schemes within high-resolution numerical models. The liquid water content and cloud properties, varying from shallow to convective clouds, are highly sensitive to autoconversion rates, and their sensitivity is closely linked with model biases. Four different (Kessler, KES; Liu-Daum, LD; Khairoutdinov-Kogan, KK; Lee-Baik, LB) autoconversion parameterization schemes have been utilized in the WRF model for simulating two thunderstorm events over India. The LD, LB and KK autoconversion rates exhibited closer performance and demonstrated a better probability distribution of raindrop size and precipitation compared to KES. The study highlights the importance of proper choice of autoconversion rates in numerical weather prediction models.
(Bhowmik M., Hazra A., Atmospheric Research, 315: 107859, April 2025, DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2024.107859, 1-11)
Read MoreNew Publications
Decadal seasonal characteristics of precipitation microphysics over the Western Ghats using the space-borne precipitation radar
(Amit Kumar, Srivastava Atul K., Mehrotra B.J., Srivastava M.K., Pattanaik D.R., Atmospheric Research, 315: 107894, April 2025, DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2024.107894, 1-12)
Influence of land use land cover and topography on lightning distribution over north and north-east Indian region
(Potdar S.S., Siingh D., Biswasharma R., Gautam A.S., Singh R.P., Journal of Atmospheric and Solar Terrestrial Physics, 268: 106460, March 2025, DOI:10.1016/j.jastp.2025.106460, 1-12 )
Trends in extreme rainfall events over Northeast India: A novel perspective
(Singh Shikha, Saini A., Kumar Siddharth, Journal of Earth System Science, 134: 9, March 2025, DOI:10.1007/s12040-024-02461-6, 1-7)
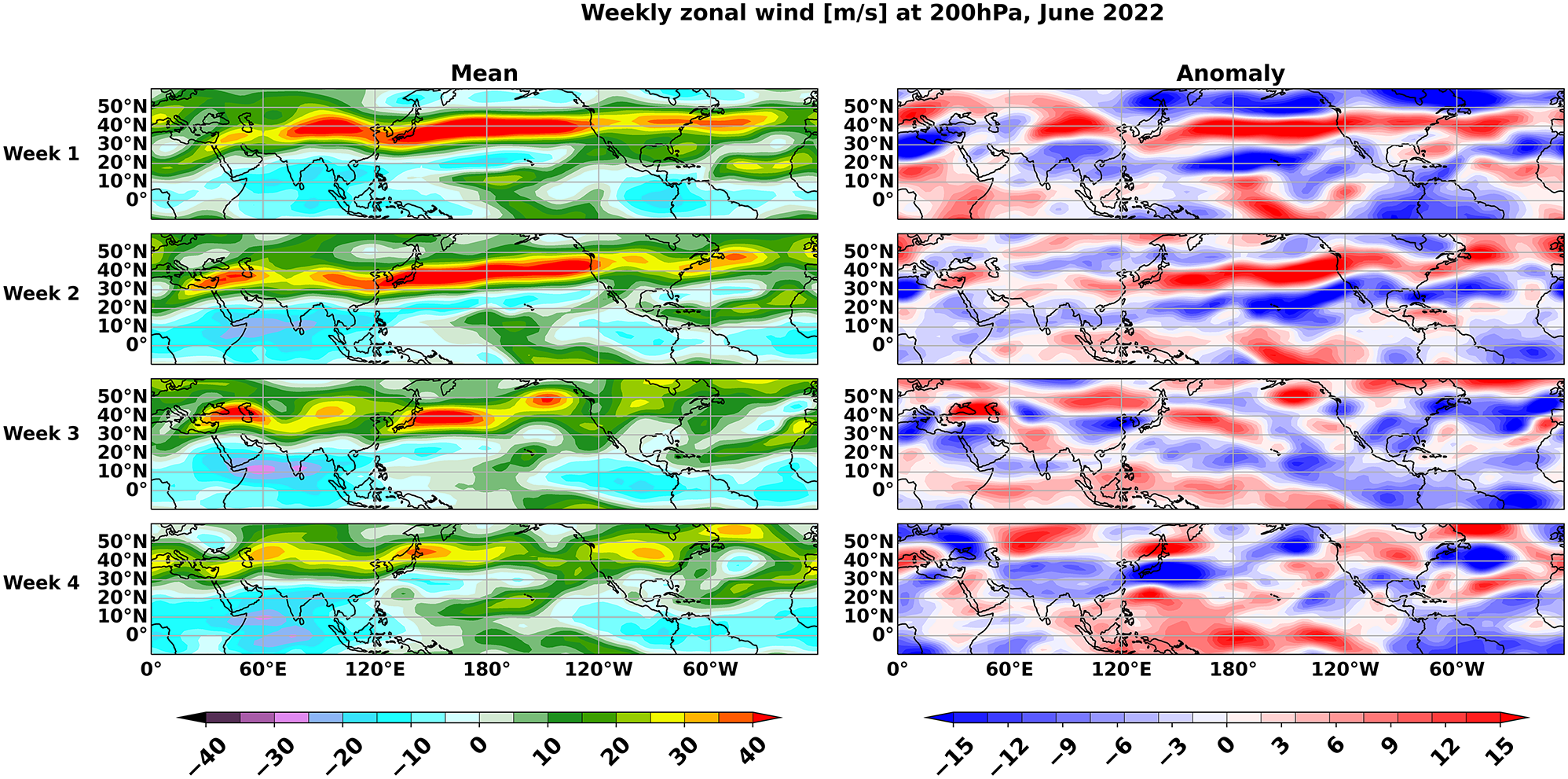
Towards Understanding the weekly rainfall variability over India in June 2022
(Mandke S.K., Vaisakh S.B., Climate Dynamics, 63: 154, March 2025, DOI:10.1007/s00382-025-07642-7, 1-13)
IITM Events

Eighth WMO International Workshop on Monsoons (IWM-8)
(17-21 March 2025)
IWM-8, the eighth workshop series under the World Weather Research Programme (WWRP) of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) organized at IITM, Pune in hybrid mode. The workshop aimed to explore recent advances in monsoon prediction, modeling, and understanding, including new tools for forecasting extreme rainfall and their societal benefits.

Inauguration of The Plant-Atmosphere Interaction Research (PAIR) Laboratory
(04 March 2025)
The Lab was inaugurated by Dr. R. Krishnan, Director, IITM, and Dr. Shiv Kumar Sharma, National Organizing Secretary, Vijnana Bharati (VIBHA). The lab is established to study the impacts of air pollution and climate change on plant health and crop yield.