Scientist Profile

Dr. Devendraa Siingh
Designation
: Scientist F
Phone
: +91-(0)20-25904287
Fax
: +91-(0)20-25865142
Email ID
: devendraasiingh[at]tropmet[dot]res[dot]in
| Degree | University | Year | Stream |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ph.D. | Banaras Hindu University | 1999 | Physics (Space Plasma Physics) |
| M.Sc. | Banaras Hindu University | 1994 | Physics |
| B.Sc. | Banaras Hindu University | 1992 | Physics |
 ELF/VLF emission in ionosphere/ magneto sphere
ELF/VLF emission in ionosphere/ magneto sphere
 Sferic and whistlers
Sferic and whistlers
 Ion and aerosol Physics
Ion and aerosol Physics
 Global Electric circuit
Global Electric circuit
 Atmospheric Electricity
Atmospheric Electricity
 Space weather
Space weather
 Sprites, Jets, Elves and anomalous electric field/TLEs
Sprites, Jets, Elves and anomalous electric field/TLEs
| Award Name | Awarded By | Awarded For | Year |
|---|
| Year | Designation | Institute |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-Present | Scientist F | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 2016-2021 | Scientist E | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 2012-2015 | Scientist D | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 2007-2012 | Scientist C | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 2006-2007 | BOYSCAST Fellow, DST | Institute of Environmental Physics, University of Tartu, Estonia |
| 2005-2007 | Scientist B | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 2004-2005 | IITM Group leader scientist | Indian station Maitri (Antarctica) |
| 2004-2005 | Junior Scientific Officer | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 1999-2004 | Senior Scientific Assistant | Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune |
| 1998-1999 | Senior Research Fellow (CSIR) | Banaras Hindu University |
| 1996-1998 | Junior Research Fellow (DST) | Banaras Hindu University |
| 1995-1996 | UGC Research Fellow | Banaras Hindu University |
Research Highlight
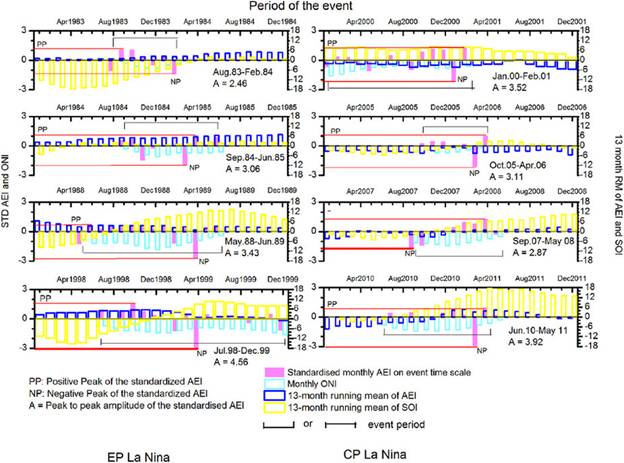
The atmospheric electrical index for ENSO modoki: Is ENSO modoki one of the factors responsible for the warming trend slowdown?
In this study new atmospheric electrical index (AEI) is proposed taking the difference in the model calculated atmospheric electrical columnar resistance (Rc) which involves planetary boundary layer height (PBLH) and aerosol concentration derived from the satellite measurements. This is the first non-oceanic index capable of differentiating between the conventional and modoki La Niña and El Niño both and may be useful in the future air-sea coupling studies and as a complementary to the oceanic indices. The correlation results show that the intensity of El Niño (La Niña) event is almost independent of its duration and the possibility of ENSO modoki being one of the factors responsible for the warming trend slowdown (WTS).


