Training in AI/ML Videos
Seminars / Lectures
IITM Publication Highlights
Unraveling the global teleconnections of Indian summer monsoon clouds: expedition from CMIP5 to CMIP6
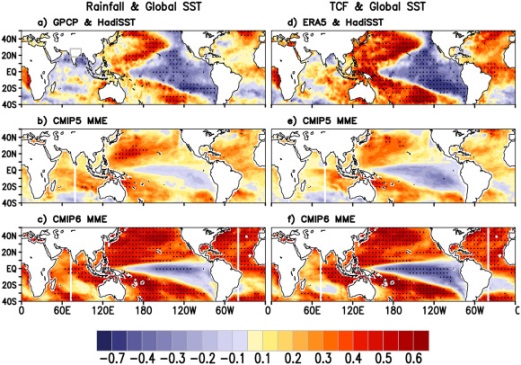 The study analysed the teleconnection of total cloud fraction (TCF) with global sea surface temperature (SST) in multi-model ensembles (MME) of the fifth and sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Projects (CMIP5 and CMIP6). The CMIP6-MME performs better than CMIP5-MME as compared to observation/reanalysis. The results establish the credibility of the CMIP6 models and provide a scientific basis for improving the seasonal prediction of ISM.
The study analysed the teleconnection of total cloud fraction (TCF) with global sea surface temperature (SST) in multi-model ensembles (MME) of the fifth and sixth Coupled Model Intercomparison Projects (CMIP5 and CMIP6). The CMIP6-MME performs better than CMIP5-MME as compared to observation/reanalysis. The results establish the credibility of the CMIP6 models and provide a scientific basis for improving the seasonal prediction of ISM.
Dutta U., Hazra A., Chaudhari H.S., Saha Subodh K., Samir Pokhrel, Verma U., Global and Planetary Change, 215: 103873, August 2022, DOI:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2022.103873, 1-12
Read MoreImproving simulation of the fog life cycle with high-resolution land data assimilation: A case study from WiFEX
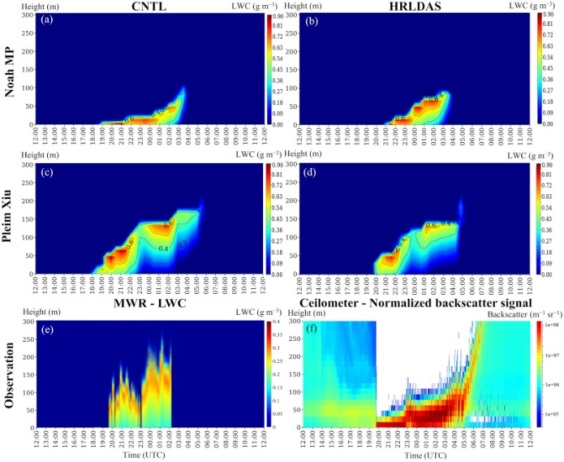 The study highlights the role of high-resolution land data assimilation in improving the prediction of radiation fog and near-surface meteorological variables. First, the quality of initial fields of soil states from reanalysis data (CNTL) and HRLDAS was examined against the observations. The HRLDAS soil product substantially reduced the wet bias in the initial soil fields during the boreal winter of 2017–2018. Second, four sensitive experiments were conducted using Noah-MP (NM) and Pleim-Xiu (PX) land-surface parameterisations in the WRF model initialized with CNTL and HRLDAS soil states. Using High-resolution HRLDASSM/ST, WRF's PX land surface scheme positively impacted fog life cycles, reducing a fog onset error by two hours and improving its vertical evolution.
The study highlights the role of high-resolution land data assimilation in improving the prediction of radiation fog and near-surface meteorological variables. First, the quality of initial fields of soil states from reanalysis data (CNTL) and HRLDAS was examined against the observations. The HRLDAS soil product substantially reduced the wet bias in the initial soil fields during the boreal winter of 2017–2018. Second, four sensitive experiments were conducted using Noah-MP (NM) and Pleim-Xiu (PX) land-surface parameterisations in the WRF model initialized with CNTL and HRLDAS soil states. Using High-resolution HRLDASSM/ST, WRF's PX land surface scheme positively impacted fog life cycles, reducing a fog onset error by two hours and improving its vertical evolution.
Parde A.N., Ghude S.D., Sharma A., Dhangar N.G., Govardhan G., Wagh S., Jenamani R.K., Pithani P., Chen F., Rajeevan M., Niyogi D., Atmospheric Research, July 2022, DOI:10.1016/j.atmosres.2022.106331, 1-16
Read MoreImpact of biomass induced black carbon particles in cascading COVID-19
 The study explores the association of biomass-induced black carbon aerosolized virus with COVID-19 in one of the top-ranked polluted hot spot regions of the world, Delhi. The aged biomass BC particles tend to aggregate and react with other compounds to grow in size, providing temporary habitat to viruses leading to the rapid increase in COVID-19 cases which declined after the crop burning stopped.
The study explores the association of biomass-induced black carbon aerosolized virus with COVID-19 in one of the top-ranked polluted hot spot regions of the world, Delhi. The aged biomass BC particles tend to aggregate and react with other compounds to grow in size, providing temporary habitat to viruses leading to the rapid increase in COVID-19 cases which declined after the crop burning stopped.
Rathod A., Beig G., Urban Climate, 38: 100913, July 2022, DOI:10.1016/j.uclim.2021.100913, 1-7
Read MoreRepresentation of moist convective processes in Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 and Phase 6 models for the simulation of Indian summer monsoon intraseasonal variability
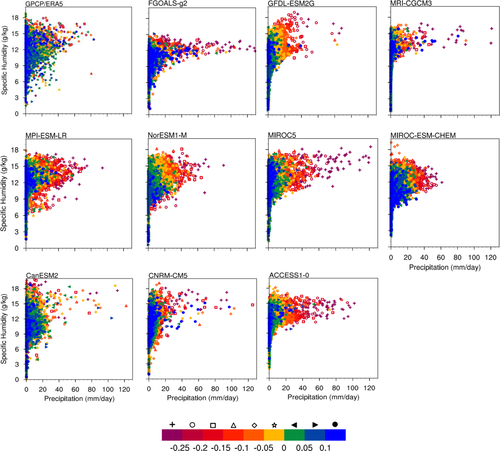 This study assesses the simulation of the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO), particularly the associated moist convective processes in 10 models from both CMIP5 and CMIP6. Among the CMIP6 models, MPI-ESM1-2-LR, FGOALS-f3-L, and NorESM2-MM exhibit better northward propagation and the associated moist processes. The models show a deterministic relationship between vertical velocity, specific humidity, and precipitation with a much higher fraction of convective rain than large-scale rain contrary to the random relationship seen in the observation. Only FGOALS-f3-L (from the CMIP6 family), which uses convection resolving precipitation parameterization produces the variability seen in the observation to a large extent.
This study assesses the simulation of the Boreal Summer Intraseasonal Oscillation (BSISO), particularly the associated moist convective processes in 10 models from both CMIP5 and CMIP6. Among the CMIP6 models, MPI-ESM1-2-LR, FGOALS-f3-L, and NorESM2-MM exhibit better northward propagation and the associated moist processes. The models show a deterministic relationship between vertical velocity, specific humidity, and precipitation with a much higher fraction of convective rain than large-scale rain contrary to the random relationship seen in the observation. Only FGOALS-f3-L (from the CMIP6 family), which uses convection resolving precipitation parameterization produces the variability seen in the observation to a large extent.
Tirkey S., Mukhopadhyay P., Krishna R.P.M., International Journal of Climatology, June 2022, DOI:10.1002/joc.7765, 1-23
Read MoreNew Publications
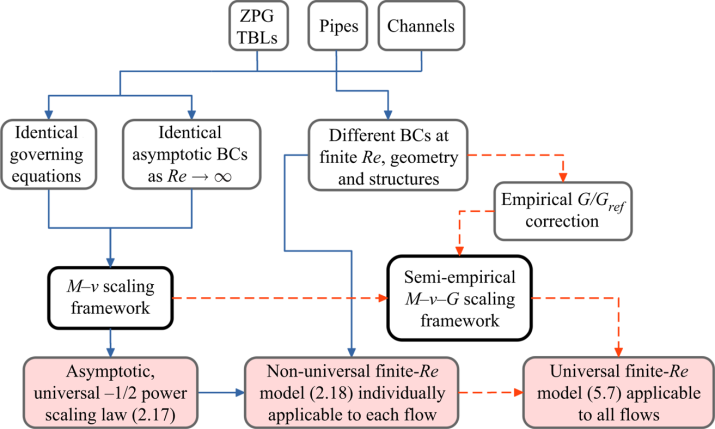
Universal scaling of mean skin friction in turbulent boundary layers and fully developed pipe and channel flows
Dixit S., Gupta A., Choudhary H., Prabhakaran Thara, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 943: A43, July 2022, DOI:10.1017/jfm.2022.463, 1-28
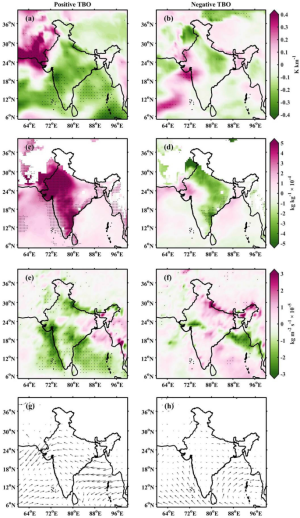
Dynamical links of convective storms associated with tropospheric biennial oscillation in the Indian monsoon regime
Murali Krishna U.V., Das Subrata Kumar, Uma K.N., Jha Abhishek K., Pandithurai G., Scientific Reports, 12: 12050, July 2022, DOI:10.1038/s41598-022-15772-9, 1-11
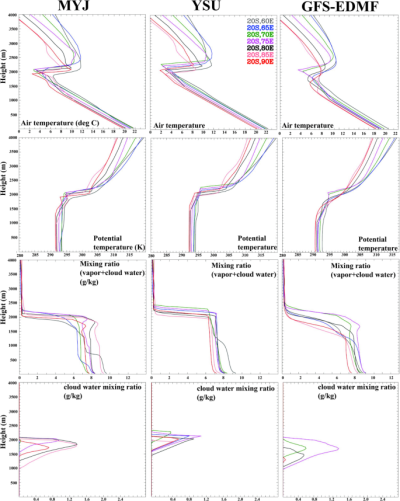
Sensitivity to PBL parameterizations on the marine layer cloud simulations in the southern Indian Ocean
Gokul T., Vellore R.K., Ayantika D.C., Krishnan R., Hingmire D., Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 134: 56, May 2022, DOI:10.1007/s00703-022-00889-3, 1-32
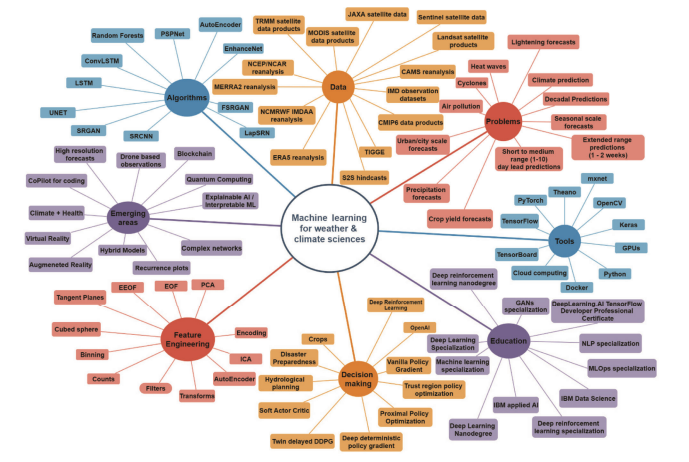
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in earth system sciences with special reference to climate science and meteorology in South Asia
Singh Manmeet, Kumar Bipin, Chattopadhyay R., Amarjyothi K., Sutar A.K., Roy Sukanta, Rao Suryachandra A., Nanjundiah R.S., Current Science, 122, May 2022, DOI:10.18520/cs/v122/i9/1019-1030, 1019-1030
PDFIITM Events

Interaction of IITM Scientists with IAF, Team (8th August 2022)
Indian Air Force, New Delhi HQ(VB) visited IITM on 08 August 2022. Air Vice Marshal Sanjay Tyagi, VCAS, Operations (Meteorology), Group Captain Amol Apte and Wing Commander Krishnan Jayadevan met Dr. R. Krishnan, Director IITM and CAIPEEX group. They also interacted with Project Directors and Senior Scientists at IITM.

SWACHHATA PAKHWADA 2022 (1-15 July 2022)
IITM, Pune has celebrated Swachhta Pakhwada from 1st July 2022 to 15th July 2022. This year various activities were implemented by the organization. The Cleanliness Drive, Awareness Campaign, Community Outreach Programs, Cleaning & Maintenance Activity, Let Us Go Green Initiative, Follow Cleanliness to Kill Tomorrow Diseases Program, Vaccination Drive etc.